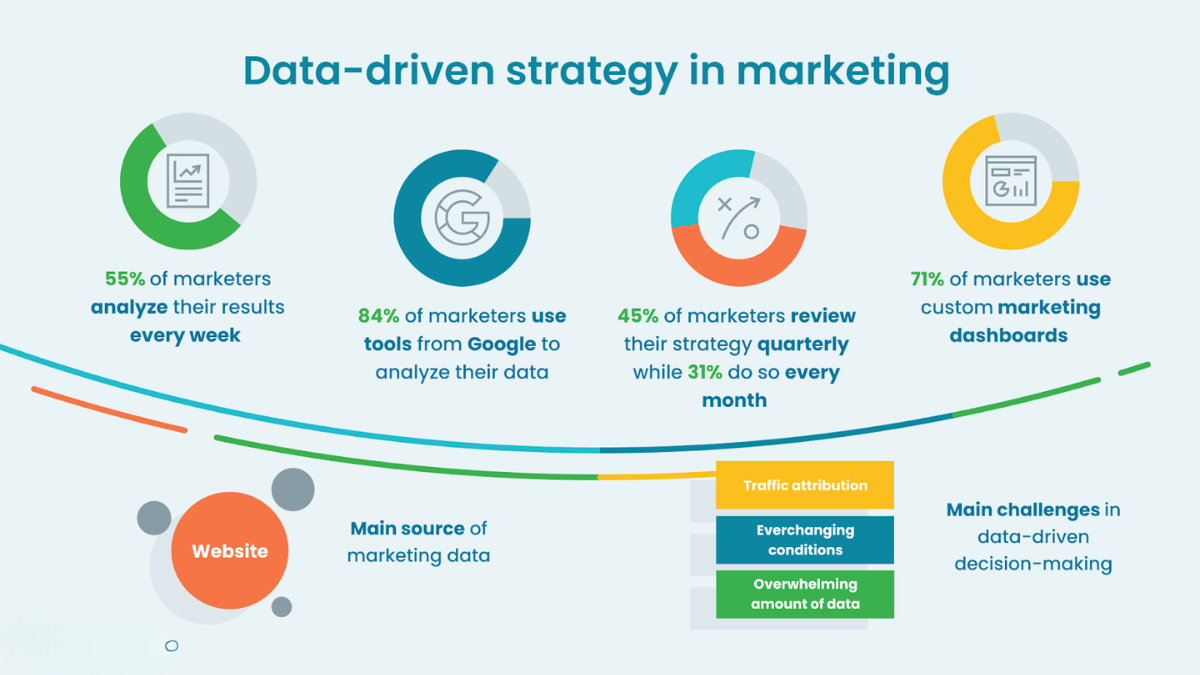
Introduction
In today’s competitive market, businesses can no longer rely solely on intuition or outdated sales methods. The future belongs to those who harness the power of data to make informed, strategic decisions. A data-driven strategy allows organizations to uncover hidden patterns, understand customer behavior, and refine their sales approach for maximum impact.
By placing data at the center of sales operations, companies can improve decision-making, boost efficiency, and, most importantly, drive more sales.
What Is a Data-Driven Strategy?
A data-driven strategy is the practice of collecting, analyzing, and leveraging data to inform and optimize decision-making. In sales, this means using customer insights, performance metrics, and market trends to shape tactics that resonate with prospects and convert leads into loyal customers.
Rather than making guesses, a data-driven strategy ensures every action is backed by evidence, leading to more predictable and scalable results.
Key Benefits of a Data-Driven Sales Strategy
1. Improved Lead Targeting
Data provides detailed insights into who your ideal customers are, what they need, and how they behave. This enables sales teams to focus on the most qualified leads, reducing wasted time and effort.
2. Personalized Customer Engagement
With access to demographic, behavioral, and transactional data, teams can tailor messages and offers to individual prospects, increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
3. Enhanced Sales Forecasting
Accurate historical data helps businesses forecast future performance with greater precision. This allows for better resource planning, budget allocation, and goal setting.
4. Real-Time Adjustments
By analyzing real-time data, sales teams can quickly identify what’s working and what’s not. This flexibility helps them pivot strategies mid-campaign to boost effectiveness.
5. Increased Efficiency
Data highlights inefficiencies in the sales process, allowing for automation, streamlined workflows, and quicker decision-making.
Steps to Build a Data-Driven Sales Strategy
1. Define Clear Objectives
Start by setting specific, measurable goals. Whether it’s increasing monthly revenue, reducing customer churn, or shortening the sales cycle, clarity in objectives helps determine what data to collect and how to interpret it.
2. Identify Key Sales Metrics
Some essential metrics include:
- Lead conversion rate
- Sales cycle length
- Customer acquisition cost
- Win/loss ratio
- Average deal value
- Revenue per rep
Monitoring these metrics provides insight into sales performance and areas for improvement.
3. Collect Data Across Multiple Channels
Gather data from all customer touchpoints, including:
- Website analytics
- Email campaign results
- Sales call outcomes
- Customer support interactions
- Social media engagement
- Purchase and payment history
The more comprehensive the data, the more accurate and actionable your insights will be.
4. Clean and Centralize Your Data
Messy, incomplete, or duplicate data can lead to false conclusions. Clean your data regularly and centralize it in a single platform where it’s easily accessible to your sales team.
5. Use Data to Segment Your Audience
Divide your customers into segments based on shared traits such as industry, buying behavior, or location. This helps in creating targeted campaigns and messaging tailored to each segment.
6. Automate Where Possible
Automated tools can assist in capturing, organizing, and analyzing data. They also help in triggering sales actions such as follow-up emails, lead nurturing sequences, and reporting without manual intervention.
7. Leverage Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast future outcomes. It helps sales teams anticipate customer needs, prioritize high-value leads, and proactively address potential challenges.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
1. Data Overload
Too much data can lead to analysis paralysis. Focus on the metrics that directly impact your sales goals and ignore irrelevant figures.
2. Poor Data Quality
Ensure data is accurate and up-to-date by implementing regular checks and validation processes.
3. Lack of Skill or Training
Not all sales professionals are data-savvy. Provide ongoing training to help your team understand how to interpret and act on data insights.
4. Resistance to Change
Adopting a data-driven approach may require a cultural shift. Communicate the value of data clearly and involve your team in the process to encourage buy-in.
Practical Use Cases of a Data-Driven Strategy
- Email Optimization: Analyzing open and click-through rates to improve subject lines and content.
- Call Prioritization: Using engagement scores to determine which leads to call first.
- Content Personalization: Delivering customized case studies or demos based on industry or interest.
- Churn Prevention: Identifying patterns in customer complaints or reduced engagement to intervene early.
- Territory Planning: Using location and conversion data to allocate resources more effectively.
The Future of Data-Driven Sales
As technology continues to evolve, the power of data in sales will only grow. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation are enhancing how teams gather insights and interact with prospects. The companies that succeed in tomorrow’s market will be those that fully embrace a data-driven mindset today.
Conclusion
Driving more sales isn’t about working harder—it’s about working smarter. A data-driven strategy enables businesses to make informed decisions, personalize customer interactions, and maximize efficiency. By turning raw data into actionable insights, sales teams can uncover new opportunities, close deals faster, and build stronger customer relationships.
Implementing a data-driven strategy is an ongoing process, but the long-term benefits make it an essential component of any modern sales approach.
FAQs
Q1: What kind of data is most valuable in a sales strategy?
A: The most valuable data includes customer demographics, purchase history, behavior patterns, engagement metrics, and feedback. These data points help identify trends and guide effective decision-making.
Q2: How often should sales data be reviewed?
A: Sales data should be monitored regularly—ideally weekly for tactical adjustments and monthly or quarterly for strategic planning and forecasting.
Q3: Is a data-driven approach suitable for small businesses?
A: Yes. Small businesses can benefit significantly from even basic data analytics. Starting with simple metrics and growing over time allows them to make informed decisions without large investments.
Q4: How can teams avoid becoming overwhelmed by too much data?
A: By focusing on key performance indicators (KPIs) tied to business goals and using dashboards to simplify data visualization, teams can avoid overload and maintain focus.
Q5: What tools are needed to support a data-driven strategy?
A: Tools for data collection (like forms and analytics), storage (databases or spreadsheets), analysis (dashboards and reporting), and automation (emails and CRM platforms) are all helpful in implementing a data-driven sales strategy.